


Written by Rick

10 Factors to Consider When Selecting Diaphragm
Diaphragms are one of the most important elements of Air Operated Double Diaphragm Pump. They separate the wetted side (fluid side) of the pump from the non-wetted part (air side). Any diaphragm failure, rupture may result in fluid ingress into the non-wetted part of the pump. This may cause serious consequences – the destruction of the whole non-wetted part of the pump, air motor destruction, contamination of products, health risk to workers, contamination of the work environment, risk of fire or explosion.
Therefore, the diaphragm selection process is critical for trouble-free pump operation. Knowledge about the fluid (chemical name, formula or trade name, concentration, viscosity, temperature, specific gravity, the content of abrasive material, maximum solids size) is essential for this process to run properly. There are ten important factors to consider when selecting diaphragm for Air Operated Diaphragm Pump.
10 Factors to Consider when Selecting Diaphragm:
- Chemical Resistance to the pumped fluid for specific concentration and temperature.
- Chemical and Temperature Resistance to the fluids used during the pump cleaning process.
- Within given temperature limits. The actual working conditions of the diaphragm shouldn’t be beyond temperature limits given by the diaphragm manufacturer.
- Resistance to abrasive particles in the fluid. Rubber and thermoplastic diaphragms abrasion resistance varies considerably.
- Should not exceed limits of positive inlet pressure. Typically, PTFE diaphragms can handle in room temperature a maximum of 0,6 bar of positive inlet pressure (Net Positive Suction Head – NPSH). Rubber diaphragms typically can handle up to 2,75 bar.
- With consideration of their lifetime (estimated, the maximum number of cycles).
- Different suction capabilities. In general, rubber diaphragm materials are more efficient in suction, than thermoplastics, especially PTFE.
- The conductivity of the diaphragm material. ATEX certified AODD pumps require diaphragms that can carry an electrical charge.
- Hygienic standards. Many applications in the food, dairy, beverage, pharmaceutical and also cosmetic industry must utilize diaphragms that comply with 3A Sanitary Standards, or EHEDG guidelines.
- Costs. Diaphragms initial purchase cost and cost of ownership.
Chemical Resistance
Main Groups of Diaphragms:
- Rubber diaphragms
- Thermoplastic diaphragms
- Two-piece diaphragms
Materials chemical compatibility must be always checked in chemical resistance guide.
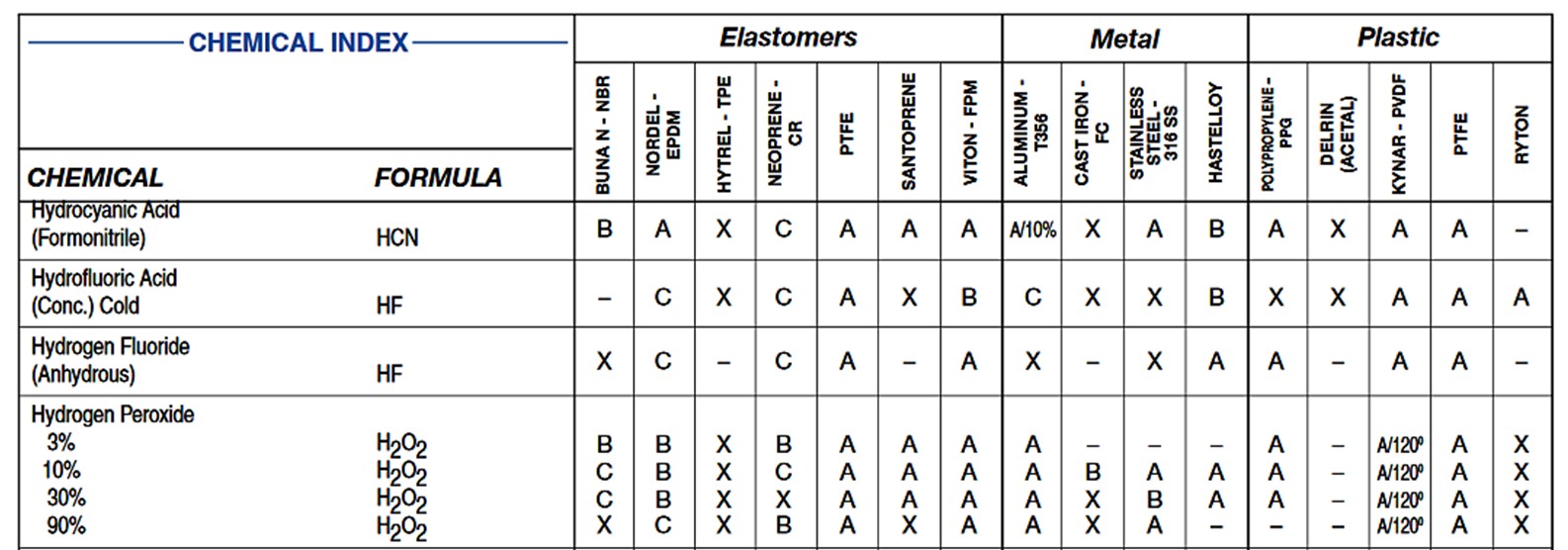
Rubber Compounds
Neoprene™ (CR)
Neoprene™ is the first successful synthetic rubber product ever made. Invented in 1930 by American DuPont Corporation is a brand name of polychloroprene.
Neoprene™ can be used as a general-purpose rubber in non-aggressive chemical applications. It has good flex life and abrasion resistance. Neoprene™ resists degradation from sun, ozone, and weather and performs well in contact with oils.
It is not resistant to: esters, ketones, acetone, strong oxidizing acids. Certain hydrocarbons can erode it. Additionally, Neoprene™ can absorb water over time.
Sanitary standard compliance versions of Neoprene™ diaphragm are also available.
Buna N (NBR)
NBR nitrile rubber is specially formulated to prevent oil attack, meaning its mechanical properties remain intact even in direct contact with oils and grease.
Buna displays excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, water, alcohols, silicone greases, lubricants, hydraulic fluids, kerosene, turpentine and motor oils.
Being a polar rubber means it is not recommended for use with harsh chemicals, acids, polar liquids like ketones, ethers, amines and ketones, halogenated hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons, and auto / aircraft brake fluids. Buna provides moderate flex life and moderate abrasion resistance.
Sanitary standard compliance versions of Buna diaphragm are also available.
Viton® (FKM)
Viton® is the registered trademark of DuPont Performance Elastomers that becomes the generic name for all FKM polymers and rubber compounds.
Viton® has excellent resistance to high temperatures, ozone, oxygen, mineral oil, fuels, hydraulic fluids, many solvents, aromatics, or chlorinated hydrocarbons and acids.
Viton® is not recommended for exposure to ketones, amines, low molecular weight esters and ethers, nitro hydrocarbons, hot hydrofluoric or chlorosulfonic acid.
Viton® possesses low gas permeability, low compression set and good mechanical properties. However, low temperatures negatively affect their flexibility.
Nordel® (EPDM)
Nordel® is a synthesis hydrocarbon rubber a product of The Dow Chemical Company.
EPDM is resistant to water and steam, alkali, mild acids, and oxygenated solvents, ozone and sunlight. It has good resistance to many corrosive chemicals – can withstand the effect of brake fluids and another phosphate ester-based hydraulic fluids. The performance of EPDM in hot water and high-pressure steam is better than in dry heat. EPDM is inherently resistant to attack by oxygen, and U.V. EPDM has very good resistance to extremely low temperatures. Typical temperature ranges: -40ºC to +100ºC for standard compounds.
EPDM diaphragms should not be used in connection with media such as mineral and vegetable oils, vegetable and animal fats, aromatic or aliphatic carbohydrates, gasoline, petroleum oil, and grease, halogenated solvents, or concentrated acids, because these substances damage the diaphragm structure and can lead to premature diaphragm rupture.
Sanitary standard compliance versions of Buna diaphragm are also available.
Thermoplastic Compounds
Santoprene® (TPO)
Santoprene® is a high-performance thermoplastic rubber manufactured by ExxonMobil Chemical. It was designed to offer chemical resistance to a wide variety of solvents and chemicals.
Santoprene® provides elastic recovery and has temperature resistance properties. It is not readily soluble in common solvents, but will swell in aromatic solvents and halogenated organic solvents. High polar fluids such as alcohols, ketones, glycols, esters, and aqueous solutions of acids, salts and bases have little effect upon Santoprene®.
Santoprene® is not recommended for: Benzene, Carbon tetrachloride, Chlorobenzene, Chloroform, Cyclohexane, Ethyl chloride, Freon, Gasoline, unleaded, Kerosene, Trichloroethylene, Lacquer, Naphtha, Nitric acid-70%, Perchloroethylene, Toluene, Xylene.
It has an excellent stroke life expectancy, good durability and abrasion resilience.
Hytrel® (TPEE)
Hytrel® is the DuPont registered trademark for its family of high-performance engineering thermoplastic elastomers.
It has exceptional toughness and resilience, high resistance to creep, impact and flex fatigue, flexibility at low temperatures and good retention of properties at elevated temperatures. It has good flex life and excellent abrasion resistance. It resists many industrial chemicals, oils and solvents. Has the longest life in non-aggressive applications.
Teflon® Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) was discovered in 1938 by the DuPont company, and it has been in commercial use since the 1940s. Teflon® trademark was registered in 1945.
PTFE has a wide variety of uses because it is extremely stable (it doesn’t react with other chemicals) and can provide an almost frictionless surface. It is used with highly aggressive fluids such as aromatic or chlorinated hydrocarbons, acids, caustics, ketones and acetates.
PTFE has no “memory” – in other words, unlike an elastomer, it does not revert to its original shape following deformation. It has a tendency towards flow distension, i.e. distortion under stress, otherwise known as “cold flow”.
Due to poor flexibility and lack of memory PTFE diaphragms have little ability to withstand excess suction lift (vacuum pressure) or positive inlet pressure, either on the suction or discharge sides.
When AODD pumps works in series or parallel, any malfunction of the pressure control system may cause excess pressure transmission to the PTFE diaphragms causing their quick rupture.
Users of pumps with PTFE diaphragms must be also aware of water hammer and dry run negative effects on the diaphragms.
Sometimes happens, that PTFE diaphragms are damaged during pump cleaning procedure. When the system is flushed or cleaned the pressure used can be higher than the normal pump operating pressure.
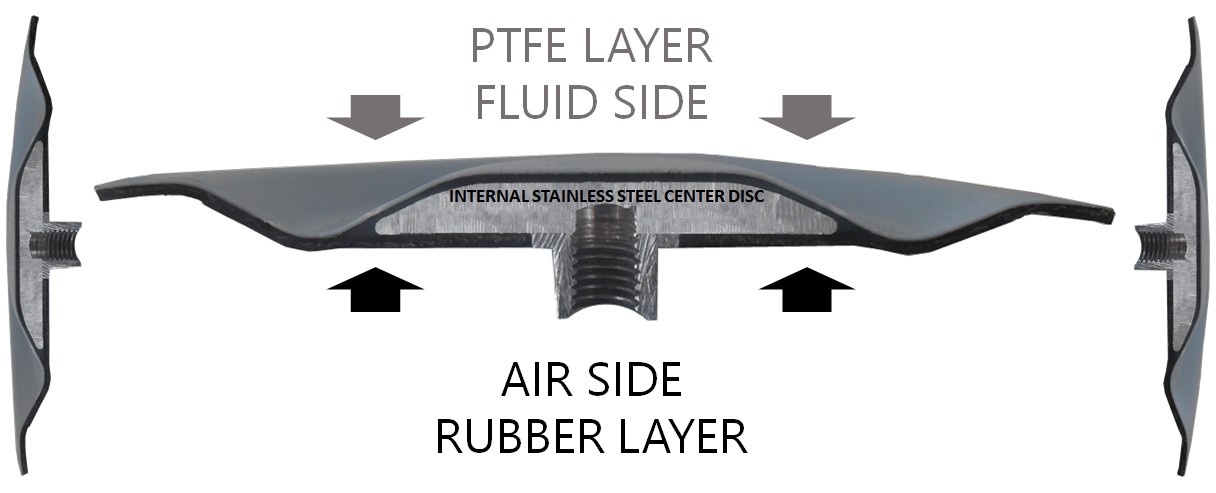
Two-piece Diaphragms
Two pieces diaphragms with two different materials (PTFE, rubber) bonded together were designed to combine the superior chemical resistance of PTFE with the flexibility of rubber. Bonded to non-elastic PTFE the rubber backing with higher mechanical durability, better flex life and memory provide extra support and resiliency to the PTFE layer.
Two-piece diaphragm with PTFE layer facing fluid and rubber layer on non-wetted side provide extended resistance to the elevated temperatures. Two-piece PTFE diaphragm with Viton® backing can be used in pumping applications, in which fluid temperature reaches 176°C.
Two-piece bonded PTFE diaphragms are widely used in Printing, Food and Beverage, Cosmetics and Pharmaceutical industries.
YTS family of two-piece bonded diaphragms is marked under the common name – SOLID ONE‐PIECE PTFE. Those diaphragms containing pure PTFE sheet on the wetted side, bonded to the rubber backing that is facing air side are a significant advancement over conventional single-layer PTFE diaphragms.
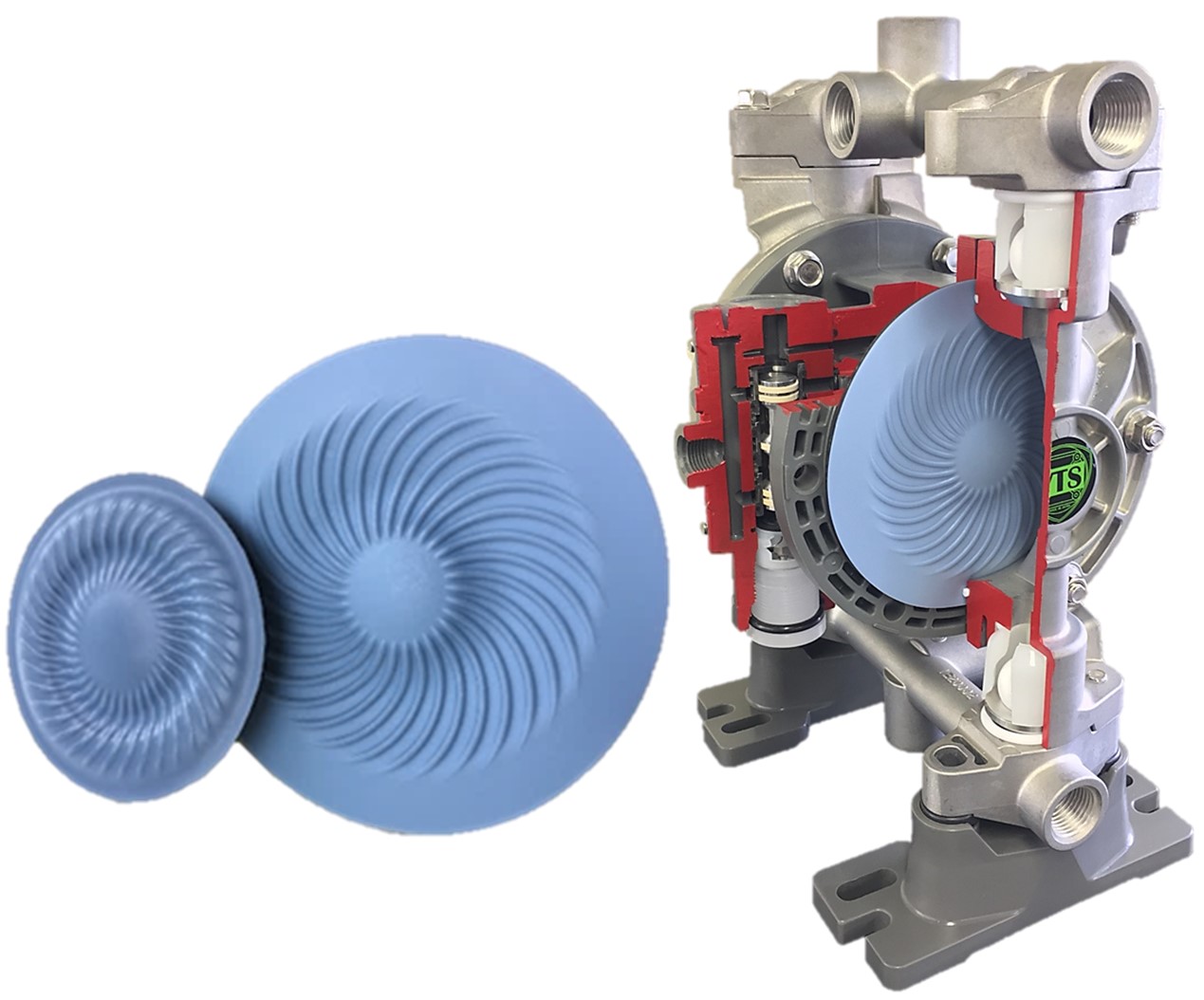
TO Diaphragms
TO two-piece bonded diaphragms in different sizes – those diaphragms have smooth, easy to clean PTFE surface. On the non-wetted side, there is a rubber layer (bonded with PTFE) and an internal Stainless Steel Center Disc.
This type of diaphragms is significantly stronger with greater flex life. They have increased pressure tolerance. They are easy to install and replace. Their smooth, easy-to-clean PTFE surface without any folds or holes makes them ideal for the printing industry. The pump must be thoroughly cleaned before changing the color of the pumped ink, to prevent any potential color contamination.
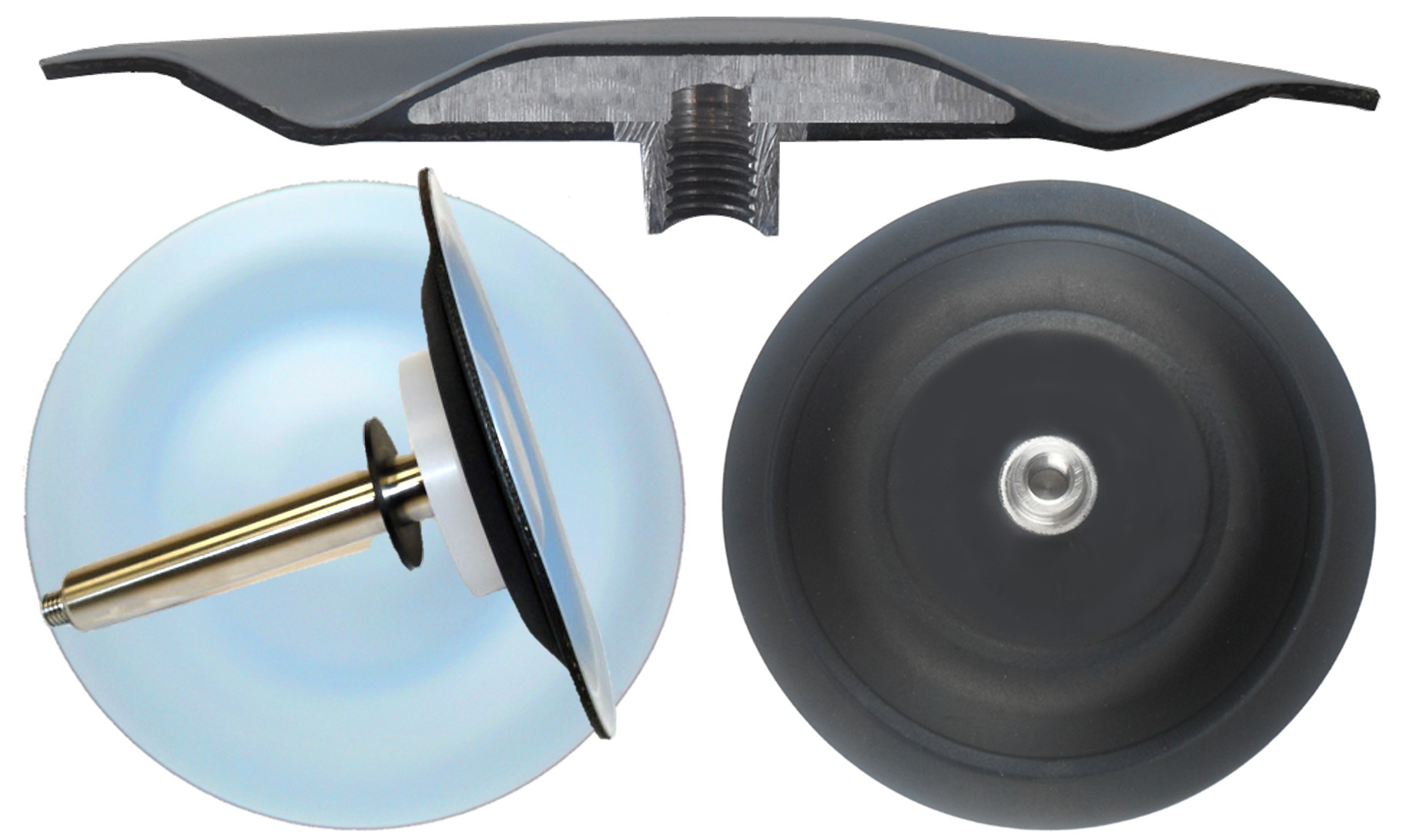

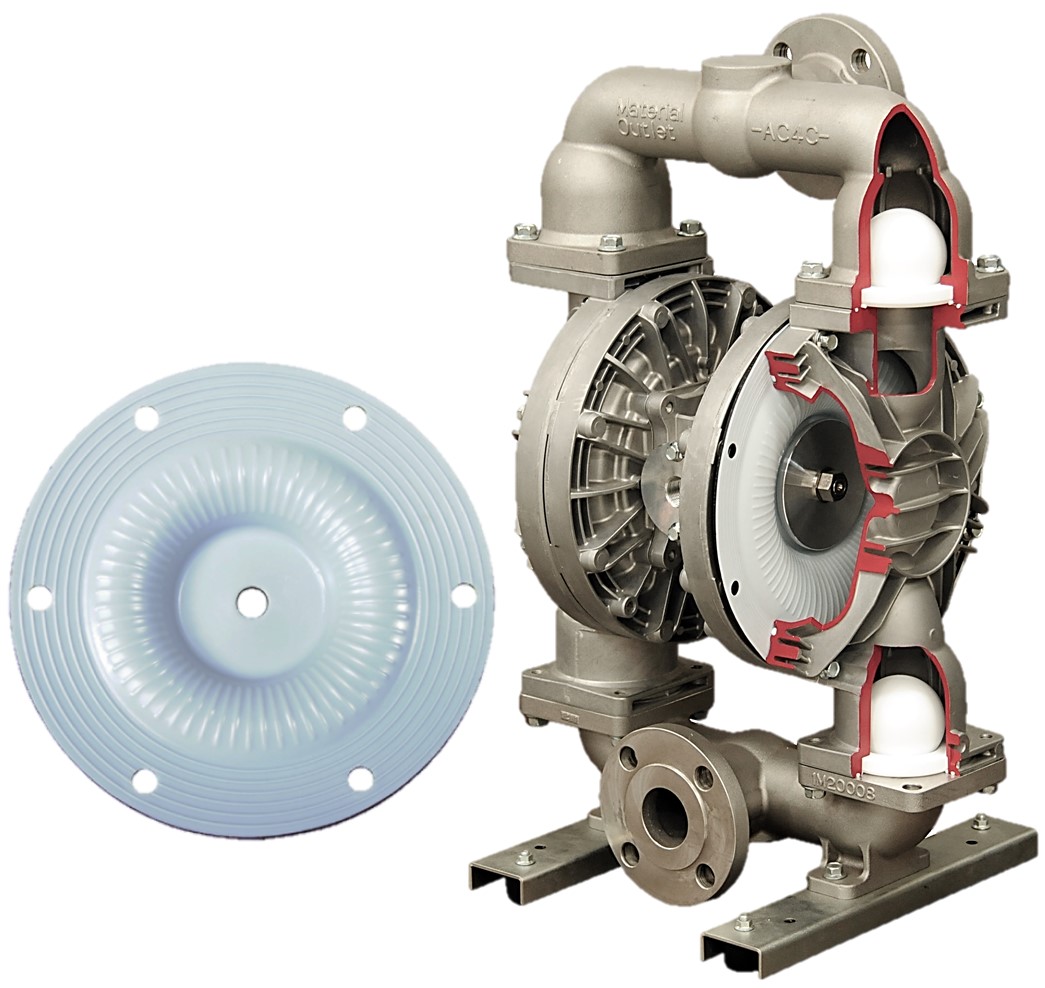
TS Diaphragms
TS two-piece bonded diaphragms in different sizes – those diaphragms have proprietary blend PTFE layer, rubber backup and internal Stainless Steel center disc. PTFE layer has spiral reinforcement ridges.
This type of diaphragms offers dramatically higher pressure tolerances. They are considerably stronger and offers greater flex life. TS diaphragms possess increased gas permeation resistance. They are easy to install and replace. TS diaphragms are used in food, beverage, pharmaceutical, cosmetic and chemical industries.
TG Diaphragms
TG two-piece bonded diaphragms in different sizes – special diaphragms with rubber backing for high-temperature applications with maximum fluid temperature up to 176°C.
Temperature Resistance
Temperature is another critical factor due to many variables. It is impossible to provide precise temperature limits for diaphragms materials for all working conditions. Factors such as:
- Diaphragm geometry varies greatly depending on the AODD pump shape and size.
- Different sizes of the diaphragms. Temperature resistance of 1/4″ and 3″ size diaphragms of the same material varies, especially when they are used in low or elevated service temperatures.
- Pump speed. In low and high temperatures working conditions pump’s speed will greatly affect diaphragm temperature resistance.
Therefore, when the pump works in low or elevated temperatures conditions the general temperature limits given by the manufacturer should be re-rated with respect for real pump operating conditions.
General maximum and minimum temperatures limits for different materials, in which diaphragms made from those materials can operate. Temperatures coupled with pressure affect the longevity of diaphragm pump components. Maximum life should not be expected at the extreme limits of the temperature ranges.
Rubber Compounds:
- Neoprene™ (CR) -18°C to 82°C
- Buna N (NBR) -12°C to 82°C
- Viton® (FKM) -29°C to 120°C
- Nordel® (EPDM) -50°C to 100°C
Thermoplastic Compounds:
- Santoprene® (TPO) -23°C to 120°C
- Hytrel® (TPEE) -18°C to 120°C
- Teflon® (PTFE) 4°C to 100°C
Two-piece diaphragms:
- TO (PTFE/EPDM backing) 0°C to 100°C
- TS (PTFE/EPDM backing) 0°C to 100°C
- TG (PTFE/Viton® backing) 0°C to 176°C
Shown temperature limits are considered as safe. They will not destroy the diaphragm, nor significantly reduce its lifetime. Diaphragm operation outside a given temperature range for specific material should always be consulted with the pump manufacturer.
Resistance to Abrasive Particles in the Fluid
Knowledge about the abrasiveness of the fluid is essential for the proper diaphragm selection. The abrasiveness of the fluid is determined by the characteristics of the solids (material hardness, size, shape), concentration and viscosity.
Knowledge about the shape and size of solids are important factors in diaphragm selection. Knowledge about the shape and size of solids are important factors in diaphragm selection. One type of diaphragm is recommended for fluids with the content of large solids with sharp edges, other types for fluids with a large concentration of small round particles.
Also, the viscosity of the fluid should be known. High viscous fluids create a protective film on pump components. Such a protective film cushions the impacts of solid particles, reducing wear (sand in oil is much less abrasive than sand in water).
Should Not Exceed the Limit of Positive Inlet Pressure.
PTFE diaphragms in room temperature conditions (around 20°C) are limited to 0,6 bar of positive inlet pressure due to their poor flexibility and low tolerances for mechanical stress. Lower temperatures will reduce this limit.
Back up diaphragms may be used in connection with PTFE diaphragms to help extend their life in severe applications.
In a very common AODD pump installation – at the bottom of the storage tank is very easy to reach and overcome the limit of permissible positive inlet pressure for the diaphragm. NPSH should be carefully calculated taking into account the height of the storage tank and the specific gravity of the fluid. Those two combined factors produce a static inlet pressure.
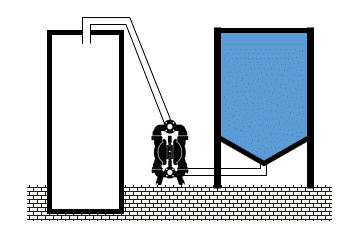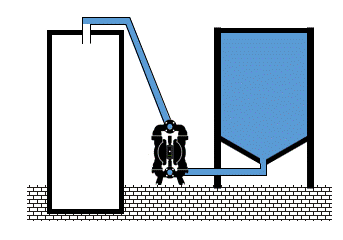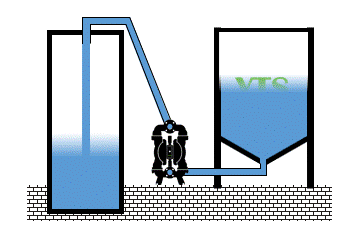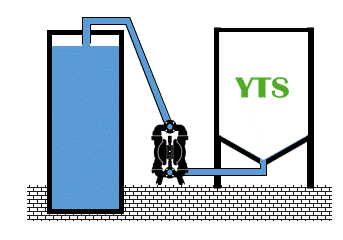
Fluid inlet positive pressure can be very destructive. When is close to the diaphragm permissible limit, shortens its lifetime radically. When exceeds limits, pump and installation can be damage.
Lifetime
The key goal in selecting a diaphragm is to entirely use the diaphragm life cycle and replace it on time, before rupture.
Many variables affect diaphragm life. For this reason, the expected longevity of the diaphragm given by the AODD Pumps manufacturer is just an estimation and should be regarded as such.
Diaphragm lifetime depends on factors such: material flexibility, chemical resistance, abrasion resistance, temperature limits, size and shape of the diaphragm, and pump’s working parameters.
However, there are occasions in which more than one diaphragm material can be selected for a specific application. If chemical resistance, temperature resistance, and resistance to the abrasive material are the same, then the maximum number of flex cycles given by the manufacturer can help the user to determine the best diaphragm material for the pump.
Suction Capability of Different Diaphragm Materials
Air Operated Diaphragm pumps are self-priming, but their suction capability depends on many factors. The type of diaphragm material is one of them.
Flexibility, shape and size of the diaphragm are important in determining the suction capacity of given diaphragm material. Suction capabilities of PTFE diaphragms are lower than other diaphragms. This factor must be taken into account when choosing a diaphragm for specific applications.
Conductivity of the Diaphragm Material
Not all diaphragms materials can carry an electrical charge. For some materials (like PTFE for example), the ability to carry an electric charge depends on the size of the diaphragm.
Larger size pumps with PTFE diaphragms require special conductive PTFE diaphragms, or installation of a second diaphragm – conductive diaphragm at the back of PTFE, on the air side.
Diaphragms Initial Purchase Cost and Cost of Ownership
Not taking into account special diaphragms, the PTFE and Viton are the most expensive diaphragm materials.
We’ve got something exciting to tell you!
HELLO SWEDISH! We’re excited to announce that we’ve just launched Swedish language support on our website! This new addition to our language family has been

Indoor Air Quality
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) – air quality within and around buildings and structures plays is of utmost importance not only for employees well-being and ability

10 Factors to Consider When Selecting Diaphragm
Diaphragms are one of the most important elements of Air Operated Double Diaphragm Pump. They separate the wetted side (fluid side) of the pump from

28 Reasons Why Use Air Diaphragm Pump
Air Diaphragm Pumps are so much versatile in design, materials, performances and functions, that they can handle most types of fluids. They are used for

Hastelloy Air Diaphragm Pumps
The primary function of Hastelloy C-22 (also known as a “superalloy” or “high-performance alloy”) is a long-lasting survival in severely corrosive, or erosion prone environments,

Too Small Size of Air Supply Line to the Air Diaphragm Pump
It is not uncommon to use too small air supply line when installing an Air Operated Diaphragm pump. Overlooking restrictions installed along the line, which
